Readability Traits of Diamonds – Feathers Clouds & Twinning Wisps
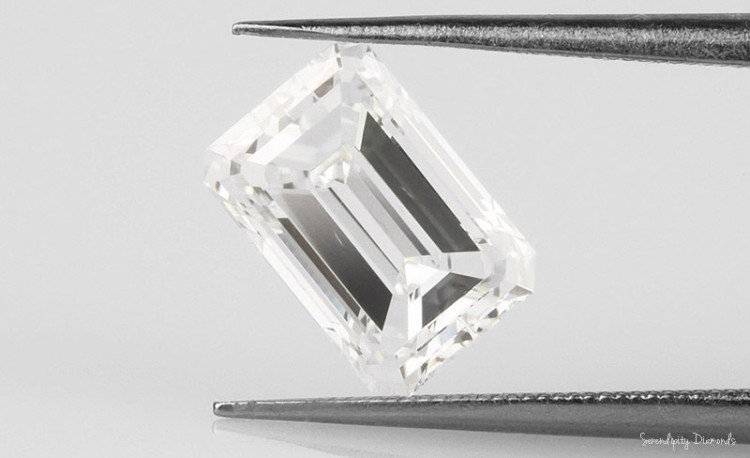

Our {photograph} reveals the visibility of a small feather seen under the desk side of an Emerald minimize diamond. Feathers signify simply one of many readability traits related to some diamonds.
Readability Traits of Diamonds
At present’s put up is dedicated to the readability traits of diamonds. There are lots of descriptions becoming for diamond inclusions. At present I’ve added every attribute with an in depth description for every attribute.
Examine most GIA diamond grading certificates, and you’ll usually see phrases corresponding to ‘feather’ or ‘twinning wisp’ for readability traits throughout the diamond or extending into the stone from the floor (inclusions) except graded Internally Flawless.
All diamonds, except Flawless and Internally Flawless diamonds, function inclusions. Relying on the focus, laboratories assign particular readability grades to a diamond. For instance, Internally, Flawless and VVS diamond readability grades signify very clear diamonds. Conversely, I2 and I3 readability diamond grades signify low-clarity diamonds.
A-Z of Readability Traits of Diamonds.
Please word that a lot of the following readability traits will normally be very discreet, many solely seen with a 10x lens and a educated eye. When showing on a diamond certificates, they merely establish and specify the kind of inclusion.
Bearded Girdle (BG)
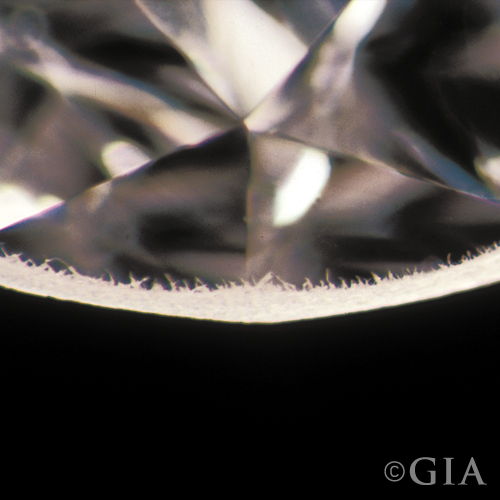

Bearded Girdle {photograph} courtesy GIA.
A bearded girdle kinds on account of the manufacture and reducing of the polished diamond. Microscopic feathers prolong from the floor of the girdle (periphery) into the diamond.
Bruise (Abbreviation: Br)
A small mark on the diamond, ensuing from impression, extends into the diamond, under the floor of the stone. These small marks usually seem the place two sides meet, and the diamond is extra uncovered to wreck.
Cavity (Abbreviation: Cv)
The place a part of a feather (see under) breaks away from the diamond, a small crack-like opening, the cavity seems.
Chip (Abbreviation: Ch)
Impression or strain may cause diamonds to chip. Chips are broken and may range in measurement and form however usually seem as breaks within the stone’s floor, usually seen on the level of the diamond, fringe of a side or culet of the stone.
Cloud (Abbreviation: Cld)
Clouds are shaped by a lot smaller inclusions grouped in a single space. Alone they’re too small to be readily seen, however collectively they’re extra noticeable however of foggier and fewer distinct.
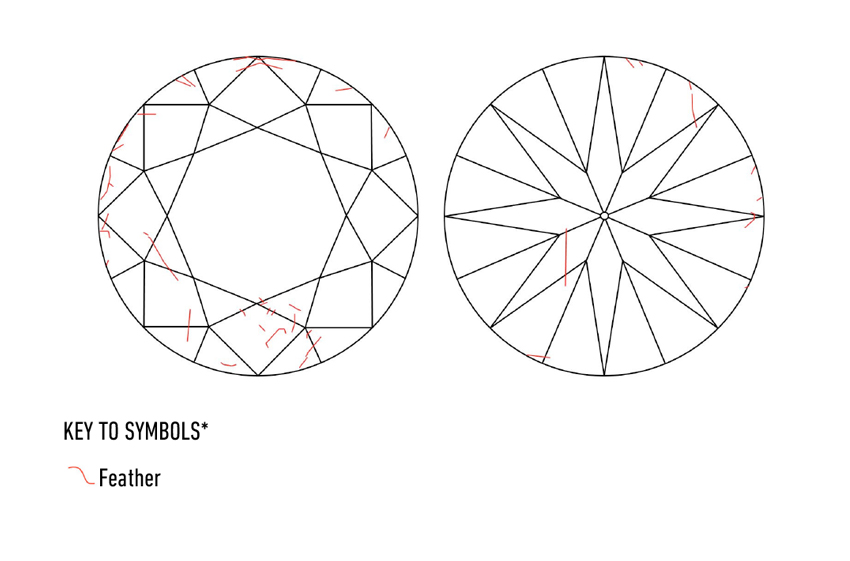
Feather (Abbreviation: Ftr)
Diamond feather is a time period used for any inside diamond fracture or fissure extending to the floor of the stone. In higher-clarity diamonds, diamond feathers could be troublesome to see, even when seen below 10x magnification.

Grain Middle (Abbreviation: GrCnt)
Brought on by distortion of the diamond crystal, showing both as mild, or darker markings throughout the diamond, normally thread-like or of pin-point look.
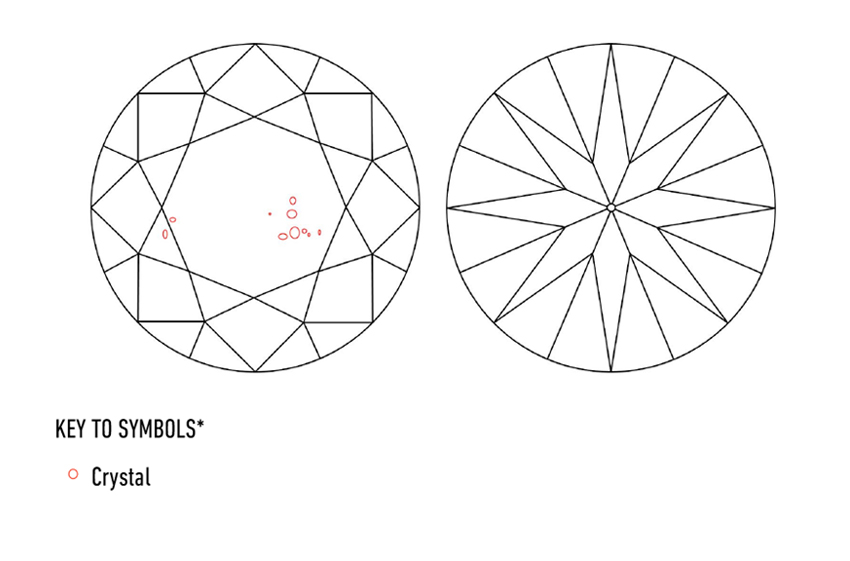
Crystal Inclusions (Xtl)
A crystal inclusion seems as a crystallised formation throughout the diamond, shaped by minerals captured through the development of a diamond.
Crystal inclusions are minerals and may seem as colourless inclusions (diamond inside a diamond), black (carbon), crimson (garnet), inexperienced (peridot) or every other mineral kind.

Indented Pure (Abbreviation: IndN)
This may be the results of a pure indent throughout the rough-diamond showing within the polished diamond’s floor. If a crystal throughout the diamond reaches and falls away from the floor upon reducing and sprucing the diamond, this may additionally reveal a pure indent throughout the floor of the stone.
Inner Graining (Abbreviation: IntGr)
Traces, Curves and inclusions seem at angles. May be white, colored or semi-transparent, brought on by irregularities throughout diamond crystal formation.
Knot (Abbreviation: Ok)
This can be a clear included diamond crystal current throughout the diamond itself, extending to the floor following the method of reducing and sprucing.
Laser Drill Gap (Abbreviation: LDH)
A positive, straight hair-like line extends from the floor of the diamond. Laser drill holes are the results of a beam of laser drilling into the diamond, usually a part of the method for readability remedy. (Which ought to be disclosed by these promoting such clarity-enhanced diamonds.) These are normally finest seen at an angle and prolong from a microscopic pin-prick measurement gap anyplace on the floor of the diamond.
Needle (Abbreviation: Ndl)
The sort of inclusion seems as a skinny, needle-like inclusion, which might range in size.
Pinpoint (Abbreviation: Pp)
A small dot-like inclusion throughout the diamond.
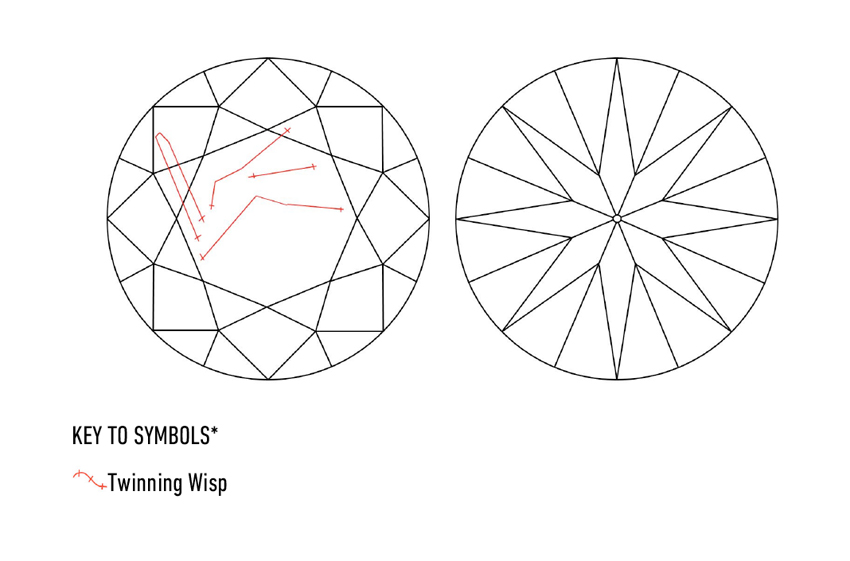
Twinning Wisp (Abbreviation: W)
Twinning wisps seem as a collection of pinpoints, clouds or crystals shaped in a diamond’s development airplane—related to crystal distortion and twinning planes.
Mainly, twinning wisps seem as tiny needles, clouds, pinpoints, and crystals organized alongside the diamond’s twinning airplane or ensuing from distortion throughout development. Our instance under reveals twinning wisps extra seen from the again of the diamond on this occasion.

How do Diamonds kind, and why are some extra included than others?
Distinctive Diamond readability traits seem in most Diamonds. These inclusions are a results of the extraordinary warmth and strain of the Earth’s crust. These circumstances alter the construction of the carbon atoms throughout the Diamond whereas it’s being shaped.
The alteration that happens is what causes Diamond inclusions to look. Relying on the circumstances, some Diamonds might have extra inclusions than others. For instance, a Diamond that has been below extra excessive circumstances might have many extra inclusions than one which has not been below such extremes.
Diamonds kind in varied environments, which accounts for the variations in color readability and measurement.
Are there some Diamond readability traits which can be worse than others?
By way of what to keep away from with Diamond inclusions, there are a number of elements to consider. You too can learn extra in regards to the readability grades of Diamond inclusions and what this implies to your Diamond.
Measurement of Diamond Inclusions
Diamond inclusions that are smaller in measurement, could make a Diamond look eye-clean. A Diamond with one or two bigger inclusions will likely be extra seen to the bare eye. Diamond inclusions that are typically more durable to see inside a Diamond can embrace pinpoints, which look identical to the purpose of a pin, and clouds, that are the identical color as the remainder of the Diamond, so are due to this fact more durable to see.
Some microscopic inclusions disperse evenly, giving the diamond the looks of being cloudy or uninteresting.
Kind of Diamond Inclusions
Black spots, cavities and chips are all inclusions which usually tend to be seen. It is because they are often bigger and darker. Black spots can appear to be frogspawn, in some individuals’s opinion, simply to provide you an instance. Chips inside a Diamond, nevertheless, will alter the outer look of the Diamond greater than something. They might additionally weaken the construction of your Diamond if they’re within the incorrect place. You may go to our earlier weblog put up on Diamond Readability Traits for extra data on the varied Diamond inclusion varieties.
Chart of inside readability traits
We’ve got listed a chart under to summarise the varied readability traits usually famous on diamond certificates.
| Readability Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Bearding | A string-like flaw shaped on the girdle (edge) through the bruting course of. Typically acceptable if not too overwhelming, because it doesn’t immediately have an effect on the diamond’s face. |
| 2. Cavity | A gap ensuing from diamond reducing, usually brought on by makes an attempt to take away flaws like feathers or crystals. Thought-about on a case-by-case foundation, particularly for increased readability ranges. |
| 3. Chip | A portion of the diamond that has chipped off, usually discovered on the rim or backside. Brought on by careless utilization or inexperienced setting. Frequent in secondhand or well-worn diamonds. |
| 4. Cloud | Clumping of pinpoints or crystals. Scattered clouds are regular, however prevalent clouds might severely have an effect on brilliance, making the diamond seem milky. |
| 5. Crystal | Pure minerals inside diamonds, coming in varied kinds. Black and inexperienced crystals can considerably impression magnificence and worth. Requires bodily inspection. |
| 6. Feather | A small crack or inclusion throughout the diamond. Visibility depends upon the angle. Extreme feathers can have an effect on sturdiness or introduce undesirable colours. |
| 7. Graining | Brought on by irregular crystal development, showing as colorless, coloured, or scratchy strains. An excessive amount of graining could make the diamond look wrinkled and muddled. |
| 8. Indented Pure | A dent under the diamond floor because of the cutter’s choice to not take away it. Frequent on edges and could be hidden with a prong setting by a talented setter. |
| 9. Needle | Lengthy and skinny needle-like flaw, normally showing as white or colorless. Clusters might have an effect on magnificence; small ones not seen on the diamond’s face are acceptable. |
| 10. Pinpoint | A small level throughout the diamond, black or white. Shouldn’t have greater than 3 factors in the identical location, or GIA will label it as a “Cloud.” Minor flaws that don’t immediately have an effect on magnificence. |
| 11. Twinning Wisp | Results of irregular crystal development, resembling a tree’s roots. Frequent in fancy shapes. A mixture of inclusions like pinpoints, crystals, feathers, and clouds, usually present in decrease readability diamonds. |
Place of Inclusions inside a diamond
Diamond inclusions on the desk of the Diamond are going to be extra seen and, due to this fact much less fascinating. Chances are you’ll not discover this an issue, nevertheless. Most jewellers have a tendency to not promote Diamonds with desk inclusions for this actual motive. Diamond inclusions additional into the Diamond can have each execs and cons, too, although. They are often nicely hidden throughout the sides. However, if they’re in simply the incorrect place, they are often mirrored within the different sides. This may make it appear to be one inclusion is multiplied many instances. Some Diamond inclusions are strategically hidden by claws, too.
Diamond cuts and Inclusions
Diamond inclusions are much less seen in some cuts of diamonds. Emerald cuts, for example, are ‘sincere’ stone cuts. Inclusions should not simply as hidden in an Emerald minimize because it has fewer sides. Alternatively, Spherical Good minimize Diamonds are extra seemingly to have the ability to ‘disguise’ inclusions. It is because they’ve extra sides.
Diamond Laboratory Grading
Diamond inclusions are also known as Diamond traits. It is because Diamond color and readability can range relying on the individual grading them. A common customary is adhered to, however this may differ ever so barely from laboratory to laboratory. For Instance, GIA (The Gemological Establishment of America) are typically very actual with their grading.
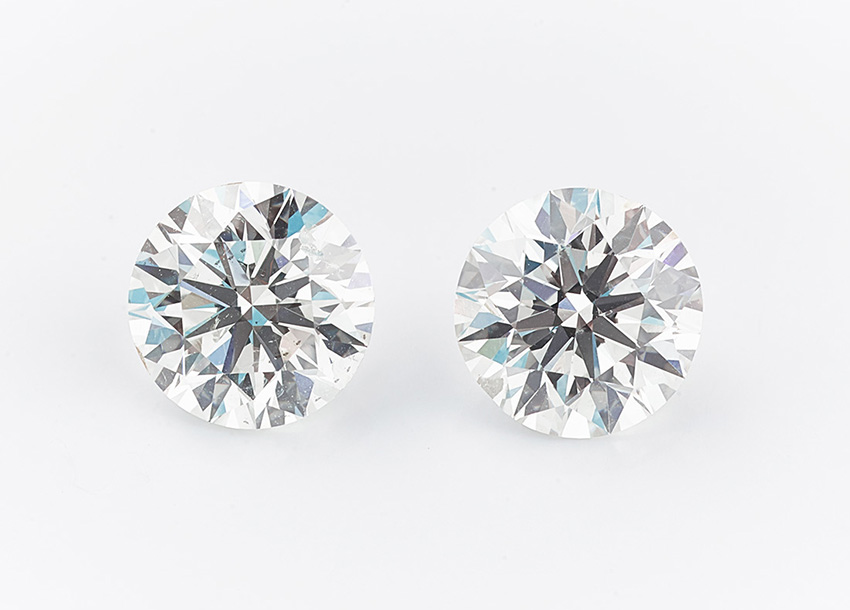

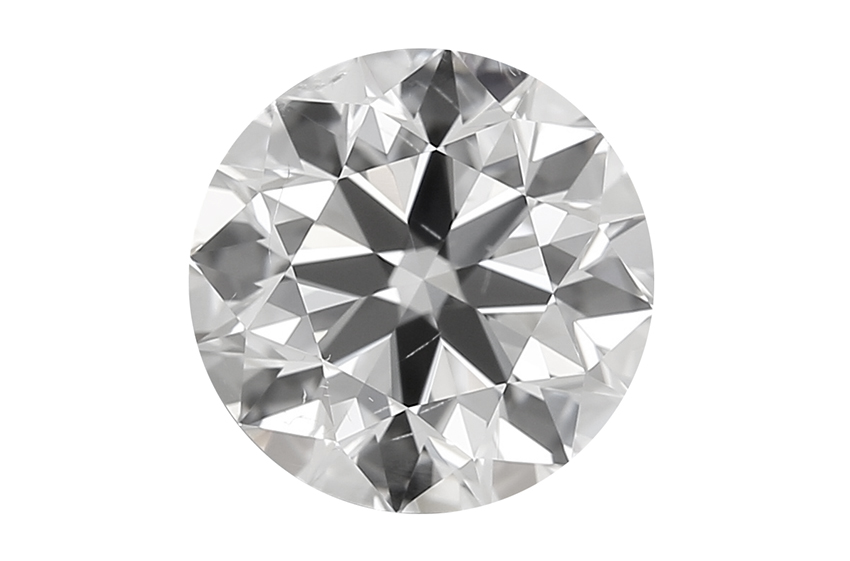
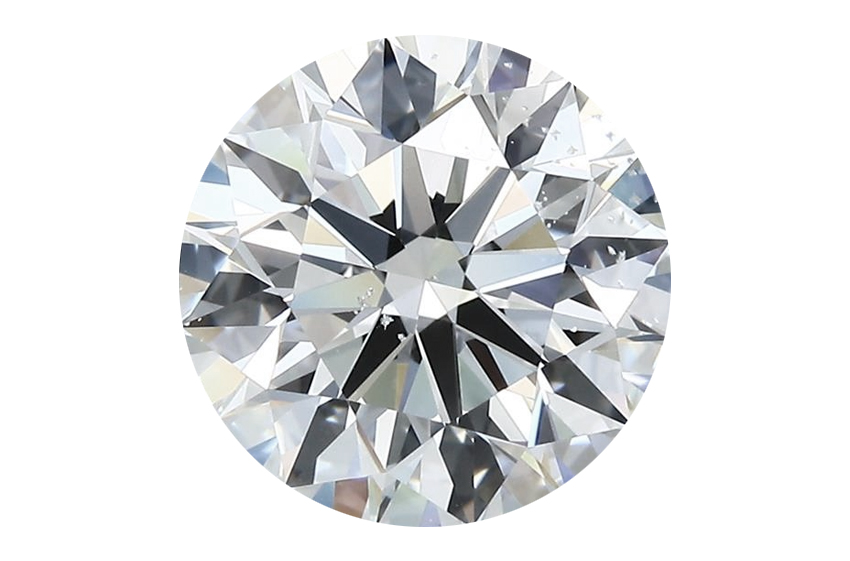
The above image reveals two Diamonds which have been graded with the very same color and readability. The one on the left has been graded by IGI.
The one on the best by GIA. GIA are typically extra strict on their grading. Subsequently the one on the best has fewer small inclusions, whereas the left-hand Diamond has extra small Diamond inclusions dotted all through.
For extra data, don’t neglect to cease by our diamond training part of the web site.
Ceaselessly requested questions
Sure, even diamonds created in a laboratory have inclusions. Lab-grown diamonds are graded in the identical means as pure diamonds. Various factors have an effect on the kinds of inclusion, such because the velocity of development and imperfections within the lab-grown tough.
First, have a look at the readability grade of your diamond. If the readability grade evaluation is VS1 or above, don’t fear in regards to the presence of clouds, feathers or crystals, which can seem invisible to the bare eye.
Sure. All lab-grown diamonds are graded for color and readability. Nonetheless, solely diamonds above 0.30-carats usually embrace a diamond certificates. Typically, most lab diamonds obtain a lot increased color and readability grades.
About Mark Johnson
My title is Mark and I am founder at Serendipity Diamonds. By day you may discover me working in our showroom—in quite a lot of roles. My work (which I really like) ranges from photographing jewelry, to writing weblog posts and serving to purchasers with my colleagues Drina, Emily and Debbie.




